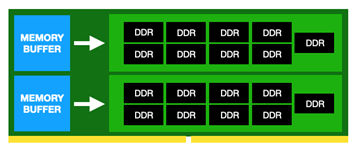
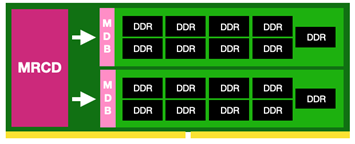
Server Buyers Guide
We provide a wide variety of servers, built to your requirements by Scan 3XS Systems. This guide takes you through all the major components of a server build and highlights areas to consider. It also covers server accessories and some wider infrastructure points too, as these may all place a part in the performance and suitability of your server.