Types of UPS
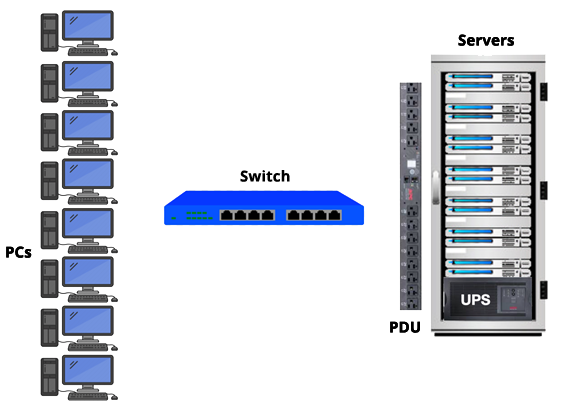
Depending on the size of the business setting and numbers of devices will determine whether a tower (free-standing) or rack mounted UPS will be the best choice. Rackmount UPS devices typically allow for more connections and offer greater expandability when it comes to battery runtime.

Tower UPS

Rackmount UPS
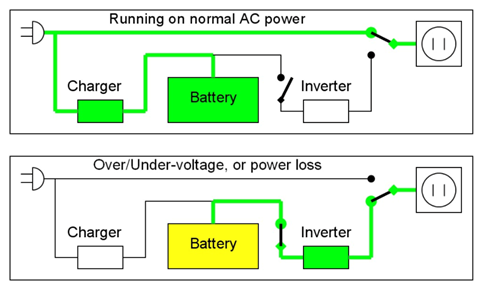
Aside from form factor, there are three main types of UPS - Offline or Standby UPS, Online UPS and Line Interactive UPS. Offline / Standby UPS is the most basic out of the three, providing only light surge protection and battery back-up. During normal operations, it gets its power from its main power source (generally an AC outlet). Once it senses that the main power source goes beyond acceptable limits or fails, it switches to the offline / standby battery where it will then go to the DC/AC inverter – as such, there will be a small transfer time between the main power source and battery. An Online UPS differs in that the DC/AC inverter is always connected on. This means there will be no transfer time between the main power source and battery, providing greater protection against
spikes, sags, electrical noise, and complete power failure.
A Line Interactive UPS has a similar design to an Offline / Standby UPS, but with properties of an Online UPS as well. A Line Interactive UPS can handle small under-voltages and over-voltages (about 20% from its standard voltage) by using a multi-tap variable voltage autotransformer or buck-boost converter. Even during these small under/over-voltages, the battery is not being used and is still being charged until there is a big under or over-voltage. Like an Online UPS there is no delay in switching power sources in the event of a failure. The three types are summarise below:
| UPS Type |
Benefits |
Limitations |
Value Proposition |
| Offline /Standby |
Low cost, high efficiency (typically 95 – 98%), compact |
Uses battery during brownouts, limited or no protection against power irregularities, impractical over 2kVA |
Best value for smaller businesses |
| Online |
Near ideal electrical output, highest protection against all power irregularities, ease of paralleling |
Lower efficiency (typically 80 – 90%), relatively more expensive under 5kVA |
Default choice for providing back-up power and protection to mission critical equipment and servers at datacentres |
| Line Interactive |
High reliability, high efficiency (typically 90-96%), reasonable voltage conditioning |
Impractical over 5kVA, does not protect against all forms of power irregularities |
Most popular UPS – ideal for for small office, web and departmental servers and/or harsh power environments |