PRESSZONE
SCAN AI AI PROJECT PLANNING PART 6 OF 7 - RUNNING MODELS
Part five of this seven-part guide focused on the training hardware and skillsets required to scale and fine-tune your model, ready for inferencing with unseen data and full-scale deployment.
However, for more complex algorithms such as large language models (LLMs) and Generative AI deployments, training workflows often require hybrid environments where dataset movement and model integration into other workflows is key.
Computing at scale
During training the AI model learns from data in order to make decisions or predictions, but when it comes to large-scale AI models, the training step differs from the normal process. Distributed computing and parallelism are key strategies for decreasing training times and handling the extensive data involved in large-scale AI models. The main distinction between distributed computing and parallelism lies in their scope and implementation.
Parallelism speeds up data processing by simultaneously performing multiple tasks on the dataset - either on a single GPU system or across multiple systems. This includes data parallelism, where multiple sets of data are processed simultaneously; model parallelism, where different parts of the model are processed on different machines; and pipeline parallelism, where different stages of the model are distributed across multiple processors for simultaneous processing.
Distributed computing, on the other hand, refers to the specific use of multiple systems—a network of interconnected computers or a cluster—to handle and analyse large amounts of data, with the results from each system aggregated to form the final output. Often distributed computing and parallelism work in tandem. Distributed computing serves as the outer layer of the training structure, processing vast datasets by expanding the hardware’s capacity. Parallelism serves as its inner layer, enhancing the efficiency within this expanded setup.
What you will need?

Advanced Hardware
We’ve stated AI training requires multiple GPUs. However, for LLMs or Gen AI, hundreds of GPUs may be required. Large scale clusters or POD architectures are available for this purpose comprising the number of GPUs necessary and advanced networking in the form of DPUs (Data Processing Units). DPUs contain dedicated onboard processors for hardware accelerated data transfer, compression, decompression and encryption to ensure data integrity across your cluster.
Learn More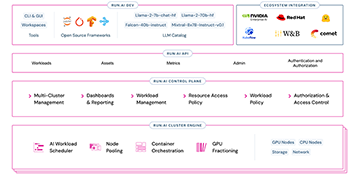
Cluster Management Software
Run:ai software allows intelligent resource management and consumption so that users can easily access GPU fractions, multiple GPUs or clusters of servers for workloads of every size and stage of the AI lifecycle. This ensures that all available compute can be utilised and GPUs never have to sit idle. Run:ai’s scheduler is a simple plug-in for Kubernetes and adds high-performance orchestration to your containerised AI workloads developed using distributed training frameworks such as TensorFlow and PyTorch.
Learn MoreWhere should I allocate workloads?
In the previous part of this guide, we recommended a hybrid on-premise / cloud strategy was the best approach to scaling AI projects both efficiently and cost-effectively. In the case of LLMs and Gen AI projects it is absolutely essential, to cope with the distributed training nature and vast amounts of data, to leverage both private and public clouds. A private cloud refers to your own infrastructure, however it may be split over numerous company buildings and/or hosted datacentre locations. Private cloud facilities may suit businesses or organisations with stringent security, privacy or regulatory requirements, as they can maintain full control over their data, infrastructure and AI operations.
In contrast public clouds can be leveraged to scale models with less upfront hardware investment. Organisations with largely non-sensitive data or few regulatory restrictions may use public cloud to benefit from near-infinite GPU scaling, retaining only their most precious data on in-house systems. It is also true that public cloud scale advantages may address short-term time pressures at any stage of the project.
Federated Learning
In use cases where data security is paramount, such as healthcare where patient anonymity is essential, a federated learning infrastructure can be deployed. Federated learning is a way to apply distributed training to AI models at scale without anyone seeing or touching your data, by processing data at source in a private cloud environment.
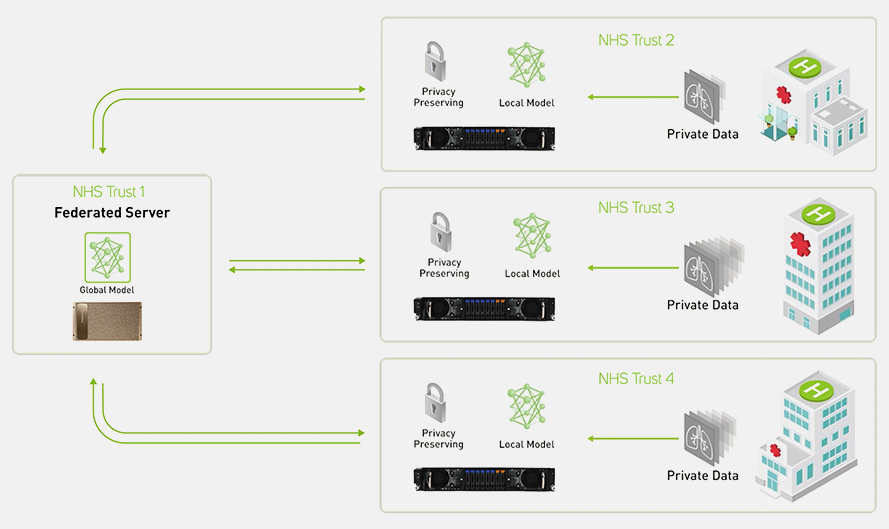
Other things to consider
AI workloads contained within an on-premise server room, isolated from the wider corporate network maybe considered relatively secure. However, when it comes to larger scale models employing distributed training and integration across private and/or public cloud environments, there are a number of other factors to consider:
- Data encryption - data, both in transit and at rest, must be encrypted using robust standards, protecting sensitive information from unauthorised access and tampering.
- Access control - strict access control measures, such as role-based access and multi-factor authentication should be implemented.
- Adversarial attacks - defend against attempts to manipulate AI models using techniques such as adversarial training and robust optimisation to improve model resilience.
- Disaster response - monitor AI systems for unusual activity or anomalies that could indicate security breaches, in conjunction with an incident response plan to quickly mitigate any security incidents.
- Supply chain security - verify the integrity of third-party tools and libraries by regularly updating and patching to protect against known vulnerabilities.
Scan’s professional services division is able to help with initial infrastructure health checks, cybersecurity audits and policy planning.
Read our 7 part AI Project Planning Guide
- Part 1 - Where do I start?
- Part 2 - Setting Expectations
- Part 3 - Data Preparation
- Part 4 - Model Development
- Part 5 - Model Training
- Part 6 - Model Integration
- Part 7 - Governance