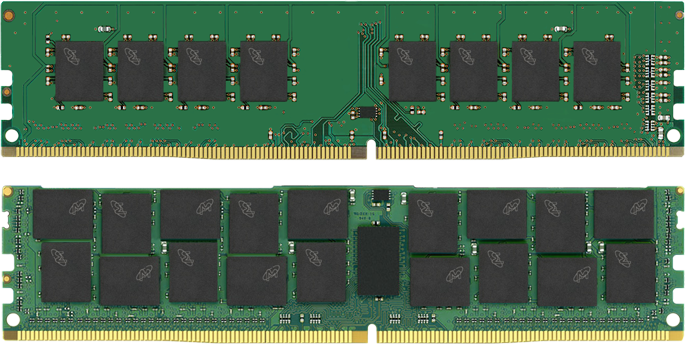
RAM / Memory Buyers Guide
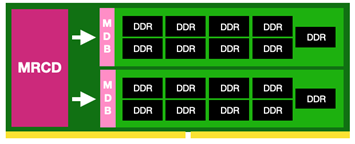
System memory, or more accurately RAM (Random Access Memory) is used by PCs and laptops to temporarily store data before it is permanently stored on an SSD or HDD. The more memory your system has, the more applications it can run at once and the faster those applications will run. With hundreds of models of memory available at any one time, it is important that you choose memory that is compatible with your system. It is also worth considering what you are planning to use your PC for, as different games and applications will benefit from varying amounts of memory.
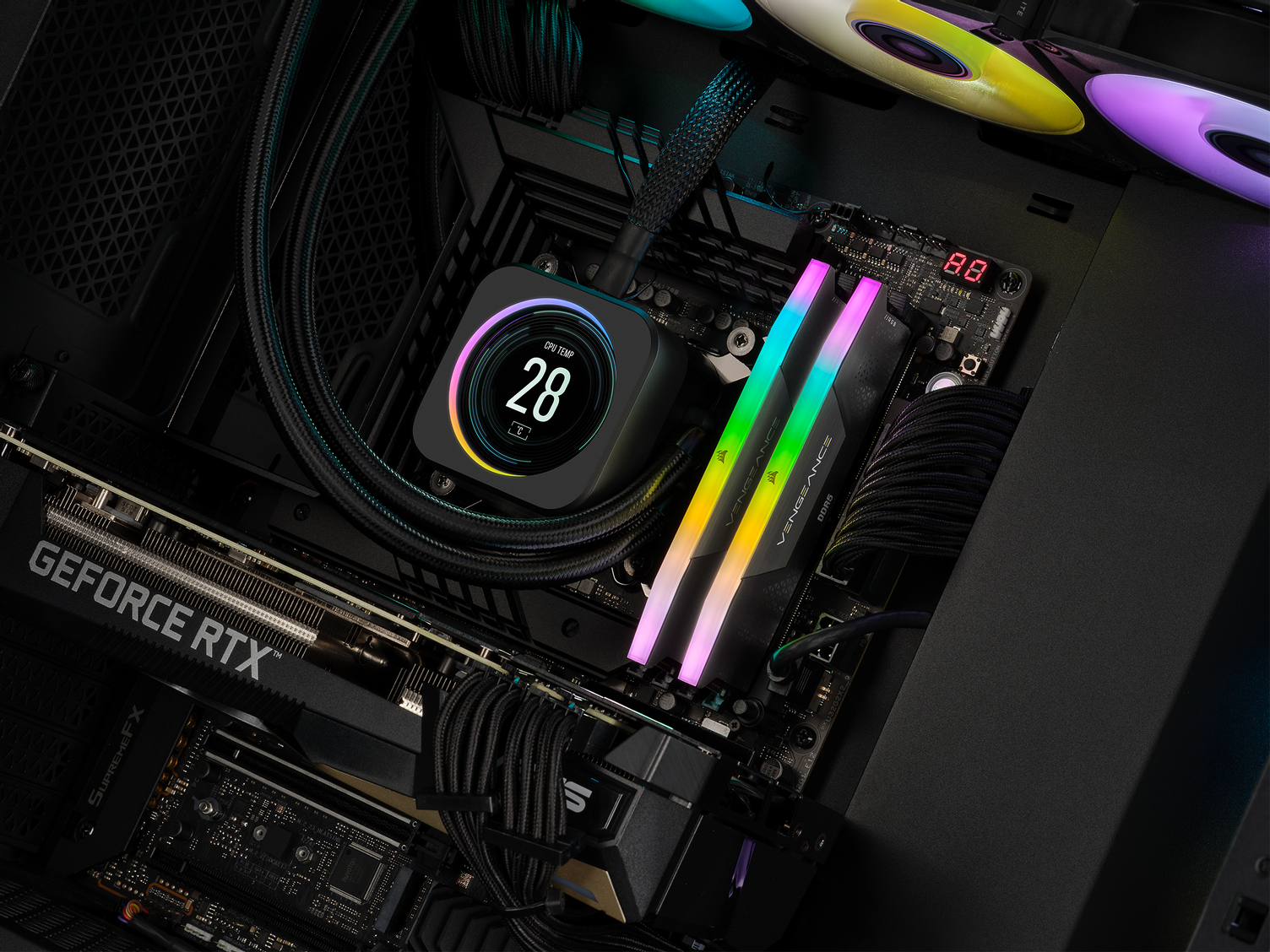
While there are dozens of different memory manufacturers, Scan recommends CORSAIR MEMORY as it is extremely reliable and available in a wide range of models.