Robots Buyers Guide
Robots are becoming increasing applicable across a wide range of industry verticals. In the same way that about ten years ago, advances in GPUs plus the ready availability of large datasets fueled AI model development; recent advances in LLMs and agentic AI models capable of reasoning, has ushered in a new dawn of physical AI, embodied by robots that can interact with the real-world and ourselves.

Selecting the right robot is crucial depending on how you intend to use it. This could be simply to perform a repetitive task in a manufacturing environment where a robotic arm would excel. However, when advanced mobility including physical security, inspection or load carrying, an AI-powered quadruped or humanoid robot is required. Although at first glance there doesn't appear to be much difference between similar looking robotic arms, quadruped or humanoid robots, their capability for customisation can be significant. This guide walks you through the range of robots available from Scan, starting with how they move, their ability to perceive their environment and their customisation.
Types of Robot
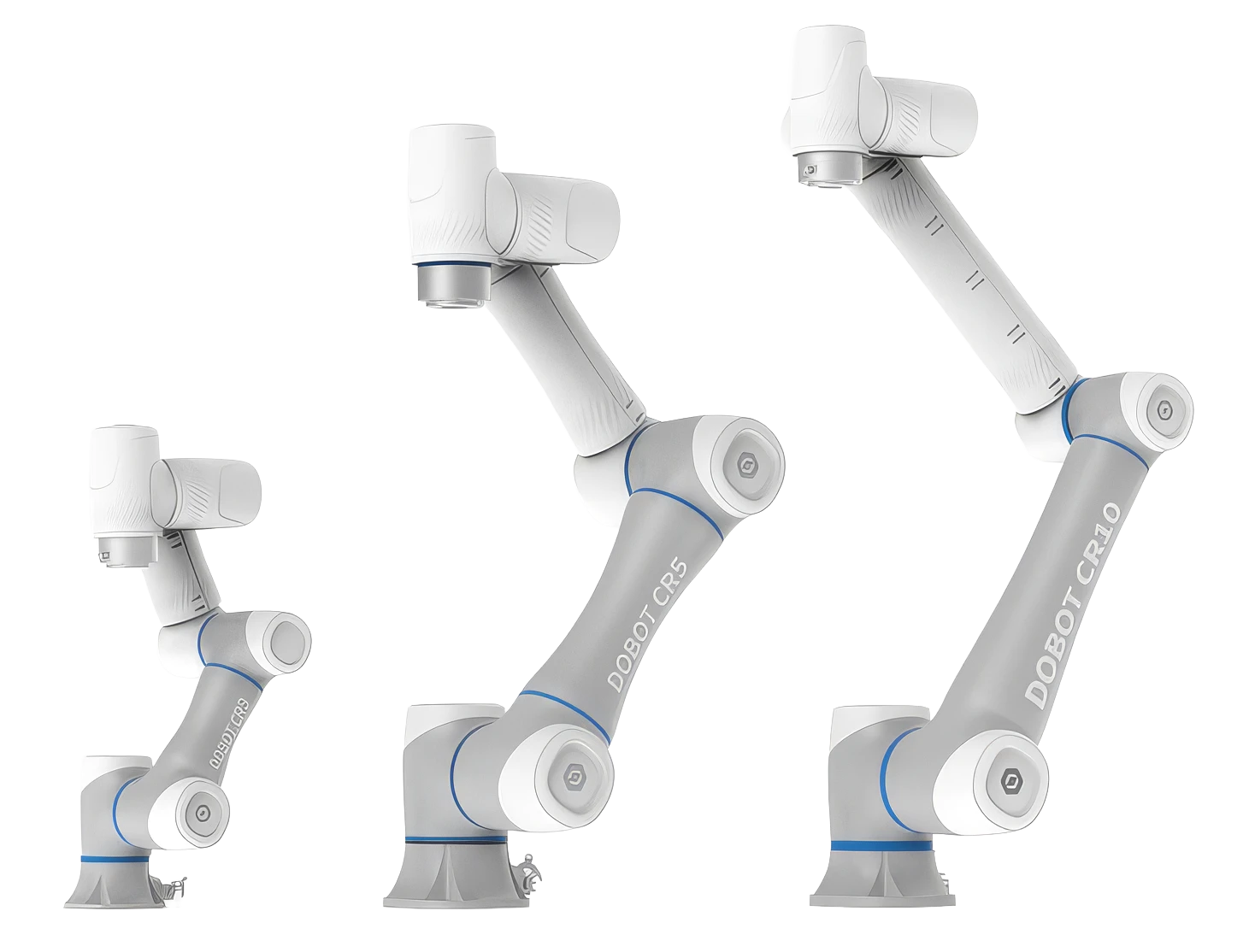
The first decision when choosing a robot should be how it moves. A robotic arm is usually deployed on a static mount with articulated joints; quadruped robots are four-legged and mimic the movement of animals such as horses or dogs, whereas humanoid robots are two-legged and two-armed and mimic the motion of humans. The choice between the three style comes down to largely what you will be used for, as each has numerous use cases, advantages and disadvantages.
Click the below tabs to explore further.
Humanoid Robots
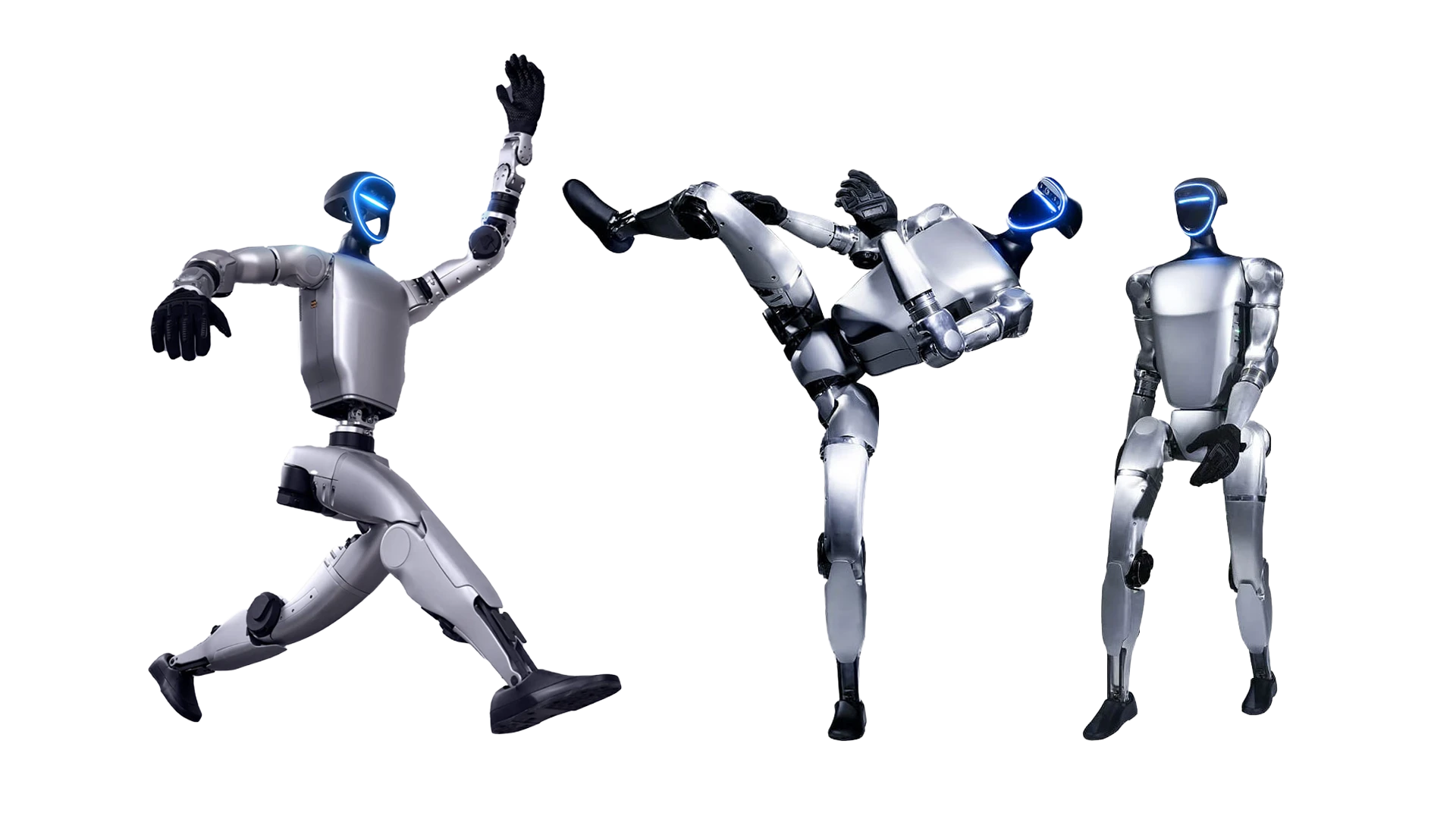
Humanoid robots, like the name suggests, have an appearance similar to that of a human. They have an upper body free for manipulation, offering dexterity and delicate motor skills, and are also highly moveable with the ability to adjust their centre of gravity. They are very energy efficient especially if performing stationary tasks and are suited to complex tasks and human-robot interaction scenarios, as their behaviour can be made very similar to that of a human.
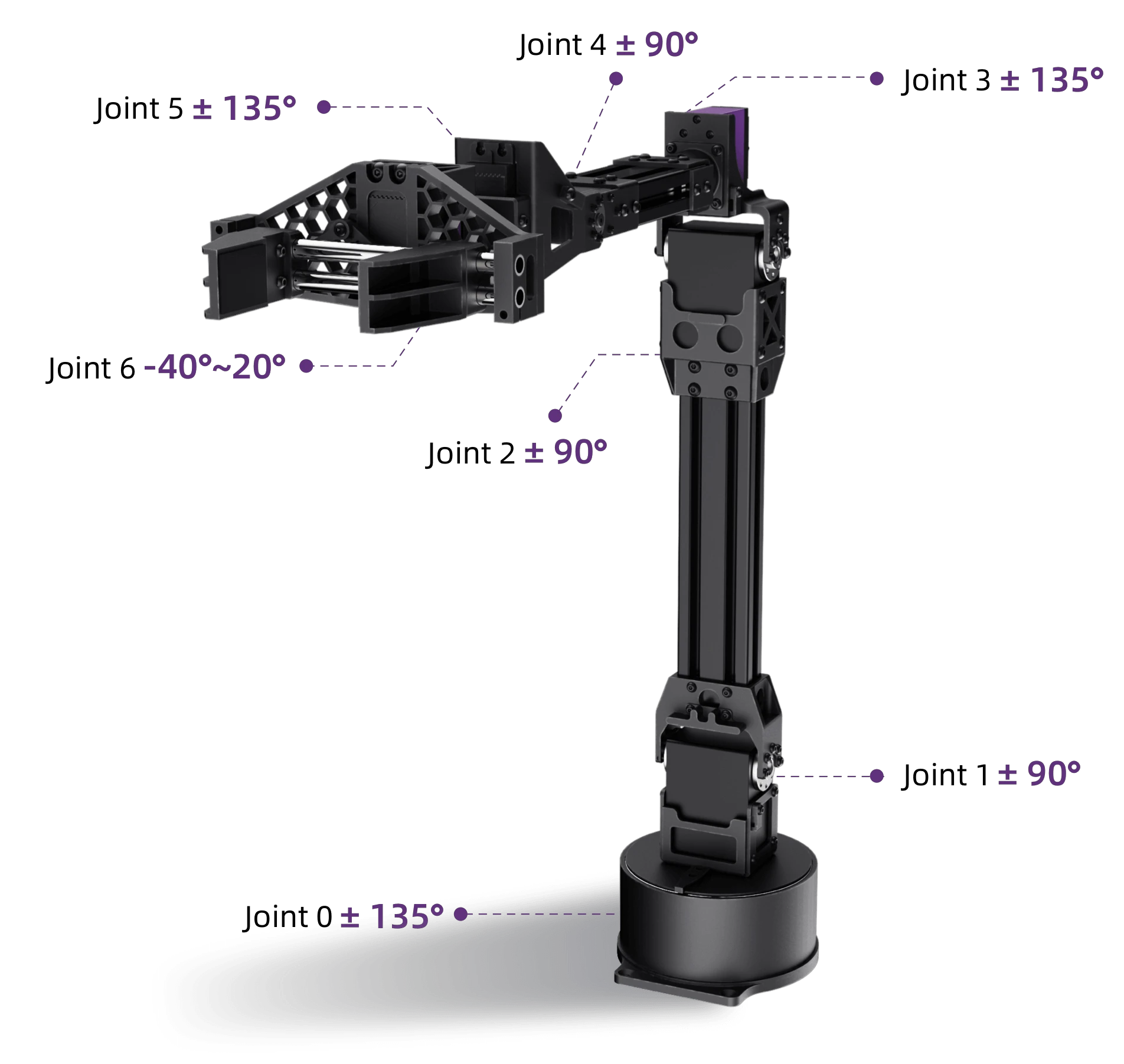
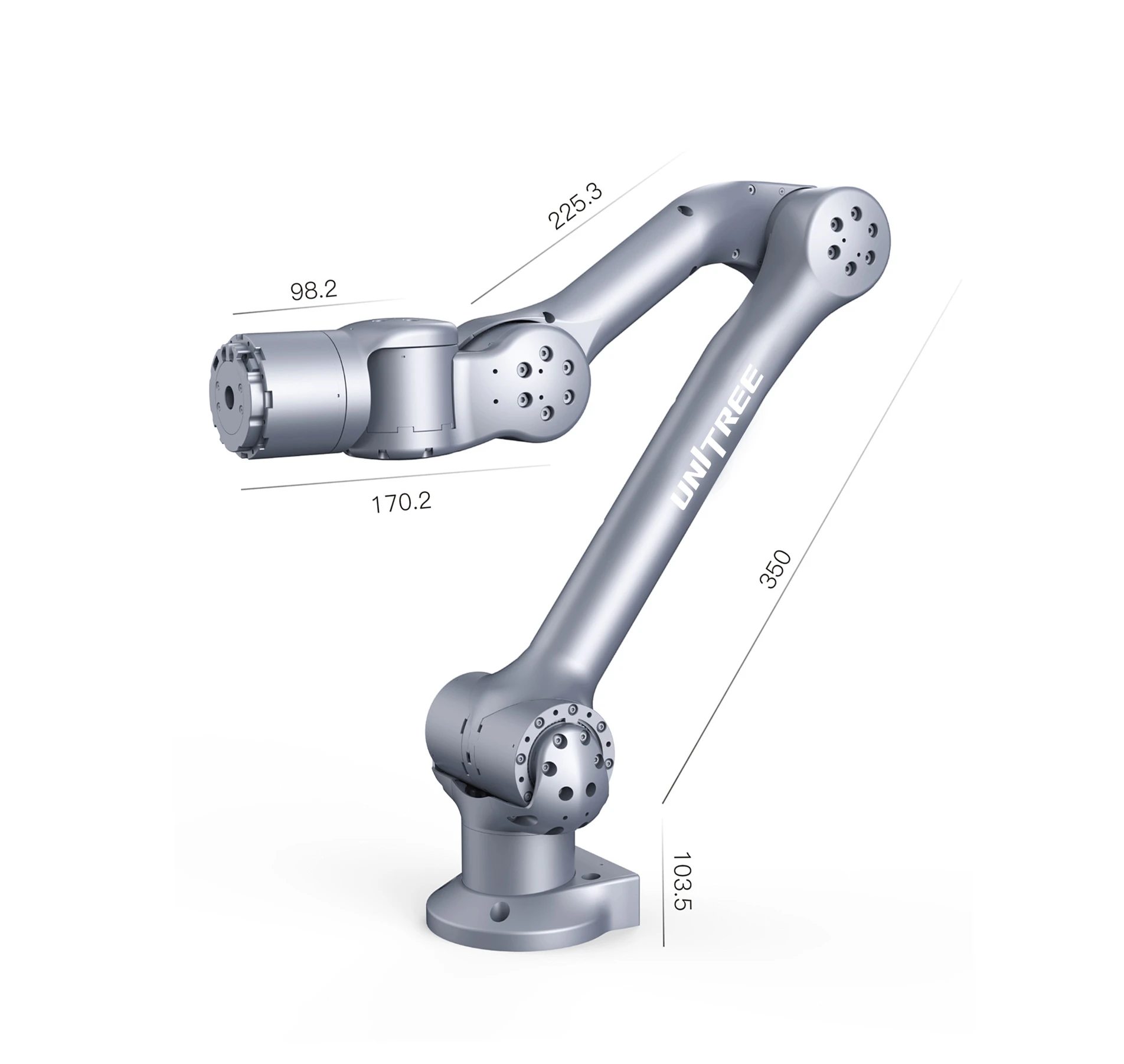
How articulate a humanoid robot is has a large impact on what it can be used for. Multiple joints, with varying degrees of freedom (DOF) and rotation capability, will allow a robot to move in a much more fluid manner with greater dexterity and flexibility. Torque levels within joint motors will further define its agility, speed and endurance. This is how rapid and / or powerful actions can be and what load-bearing capabilities the robot will have.
Click or tap any highlighted point to learn more


3D Lidar
LIVOX-MID360
Depth Camera
Intel RealSense D435i
Combined Shoulder Motors
Realisation of 3D Spacial Degrees of Freedom
Arm Degrees of Freedom
Independent Single Arm 4 (Expandable)
Core Motion Module
Maximum Torque at Joints 360 N.m
Leg Degrees of Freedom
Independent Single Leg Hip 3 + Knee 1 + Ankle 1
Mobility
Moving Speed of 3.3 Meters per Second
Hollow Joint Wiring
The Entire Machine has Internally Routed Cable Management Leaving Nothing Externally Visible.
Capabilities
The capabilities of a humanoid robot performing any given task will depend on how it senses its environment. This is achieved by a range of onboard sensors such as 360° depth cameras and 3D or 4D LIDAR with up to 128,000 points per second sampling. This combination allows advanced features such as constructing a point cloud map within a certain area, where the robot can be programmed to move autonomously, as illustrated in the video below.

This combination of joints, motors and sensors offer a huge degree of flexibility and agility, translating to natural movement, autonomous behaviours and advanced human-robot interaction opportunities.


Enhanced Programmability
Some Unitree humanoid robots have EDU in their model name, which refers to a variant that features additional capabilities. As opposed to the standard version which have a closed firmware system for basic demonstrations, the EDU models operate via an open platform so developers and researchers have the ability to unlock richer sensor capabilities and greater access control. This is achieved via the use of an NVIDIA Jetson GPU within the robot, the official Unitree SDK and the open-source ROS (robot operating system) FRAMEWORKS such as NVIDIA Isaac and GR00T.
The ROS provides a set of tools, libraries, and conventions to simplify complex robot software development by making it modular, real-time capable, secure, and cross-platform. When combined with the onboard GPU hardware it unlocks programming with C++ and Python languages, enabling features such as motion programming and state feedback. It also offers options to increase the joint DOF, directly impacting manipulation, load-bearing, whole-body control, and coordination. On some humanoid EDU models, optional dextrous hands can be added to allow for highly intricate tasks, using force-position hybrid control, so it is sensitive and reliable, and can simulate human hands to achieve precise operation of objects.
It is perhaps not surprising that the extra features of an EDU humanoid robot model do come at a cost increase, but for advanced projects and development its open-source nature, AI capabilities, greater dexterity, and potential for complex customisation may be worth it.
UNITREE G1
The Unitree G1 humanoid robot is versatile and designed for advanced research, AI development, and industrial applications. With a robust and modular design, The G1 features 23 DOF across its body six per leg, five per arm, and one in the waist allowing fluid, human-like motions driven by precise, low-inertia motors with dual encoders for accurate feedback and smooth control.
It features stereo cameras, depth sensors, and 3D LiDAR units that provide sharp visual and spatial awareness, enabling it to perceive surroundings in full 360°, map in real-time, and avoid obstacles with precision. The EDU version offers up to 43 DOF and an onboard NVIDIA Jetson Orin NX GPU for AI applications.
Wi-Fi 6 and Bluetooth 5.2 are supported as standard, allowing for over the air updates, as well as a manual remote controller to give precise manual control of over the G1.
VIEW RANGE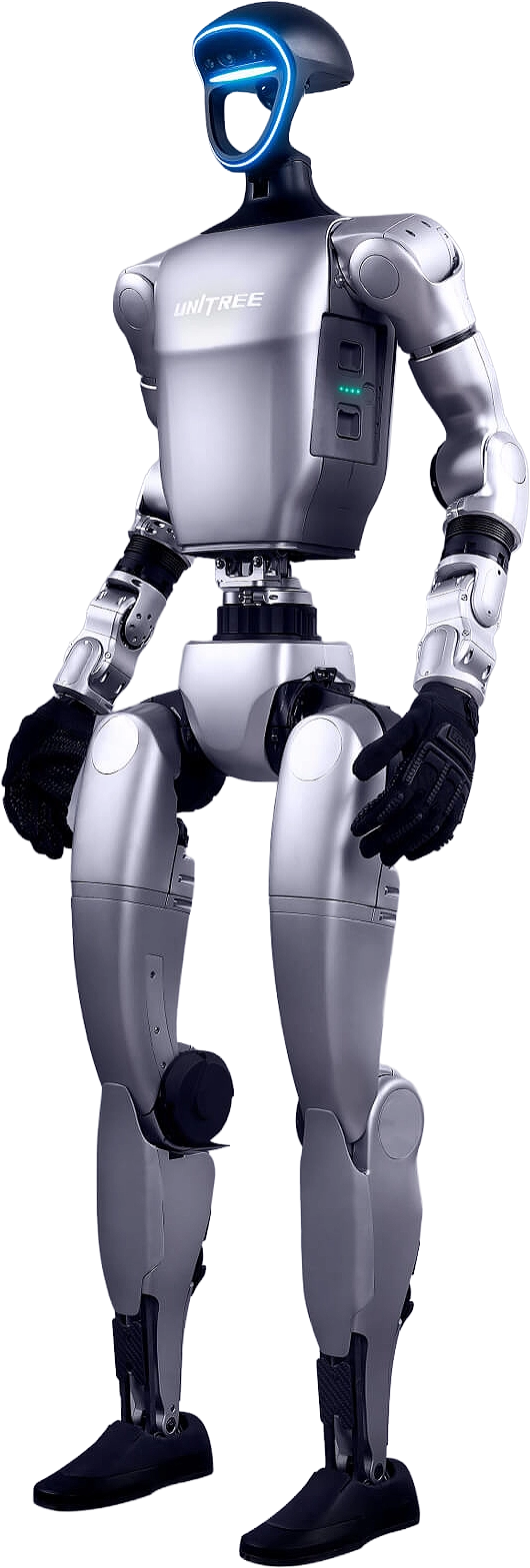
UNITREE G1-D
The Unitree G1-D is a hybrid humanoid robot featuring a standard G1 head, torso and arms, with the legs replaced by either a wheeled stand or a motorised base. The G1-D features up to 19 DOF across its body seven per arm, two in the waist, one in the column and two in the base allowing fluid, upper-body human-like motions driven by precise, low-inertia motors with dual encoders for accurate feedback and smooth control.
The base model has an HD head camera and two wrist cameras, plus an onboard NVIDIA Jetson Orin NX GPU. The flagship model gains a motorised moveable base with LiDAR and object and collision sensors. Both models can be fitted with a range of optional hands with either a two-finger gripper, three-finger claw or five-finger dextrous hand.
Wi-Fi 6 and Bluetooth 5.2 are supported as standard, allowing for over the air updates, as well as a manual remote controller to give precise manual control of over the G1-D.
COMING SOON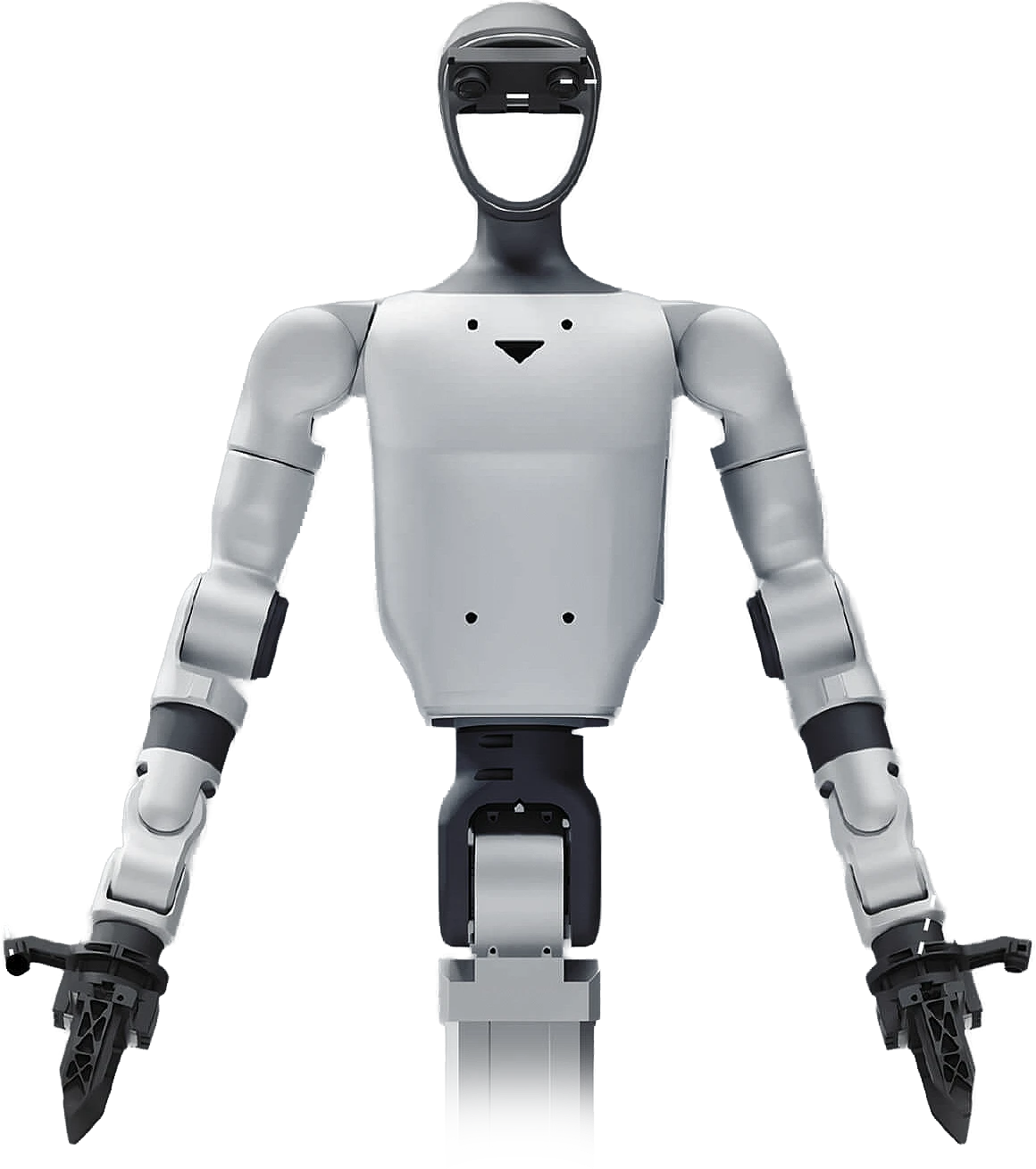
UNITREE H1
The Unitree H1 humanoid robot is versatile and designed for advanced research, AI development, and industrial applications. With a robust and modular design, The H1 features 19 DOF across its body five per leg, four per arm, and one in the waist allowing fluid, human-like motions driven by precise, low-inertia motors with dual encoders for accurate feedback and smooth control.
It features stereo cameras, depth sensors, and 3D LiDAR units that provide sharp visual and spatial awareness, enabling it to perceive surroundings in full 360°, map in real-time, and avoid obstacles with precision. The H1-2 EDU version offers up to 27 DOF and an onboard NVIDIA Jetson Orin NX GPU for AI applications.
Wi-Fi 6 and Bluetooth 5.2 are supported as standard, allowing for over the air updates, as well as a manual remote controller to give precise manual control of over the H1.
VIEW RANGE
UNITREE H2
The Unitree H2 humanoid robot is versatile and designed for advanced research, AI development, and industrial applications. With a robust and modular design, The H2 features 31 DOF across its body six per leg, seven per arm, three in the waist and two in the head allowing fluid, human-like motions driven by precise, low-inertia motors with dual encoders for accurate feedback and smooth control. The H2 also features defined facial features to appear more human-like.
It features stereo cameras, depth sensors, and 3D LiDAR units that provide sharp visual and spatial awareness, enabling it to perceive surroundings in full 360°, map in real-time, and avoid obstacles with precision. The EDU version also offers an onboard NVIDIA Jetson AGX Thor GPU for AI applications.
Wi-Fi 6 and Bluetooth 5.2 are supported as standard, allowing for over the air updates, as well as a manual remote controller to give precise manual control of over the H2.
VIEW RANGE
UNITREE R1
The Unitree R1 humanoid robot is lightweight, versatile and designed for advanced research, AI development, and industrial applications. With a robust and modular design, The R1 features up to 26 DOF across its body six per leg, five per arm and two in the waist allowing fluid, human-like motions driven by precise, low-inertia motors with dual encoders for accurate feedback and smooth control.
It features stereo cameras, depth sensors, and 3D LiDAR units that provide sharp visual and spatial awareness, enabling it to perceive surroundings in full 360°, map in real-time, and avoid obstacles with precision. The EDU version also offers up to 40 DOF and an onboard NVIDIA Jetson Orin NX GPU for AI applications.
Wi-Fi 6 and Bluetooth 5.2 are supported as standard, allowing for over the air updates, as well as a manual remote controller to give precise manual control of over the R1.
VIEW RANGE
Summary
The below table compares the different Unitree humanoid robots, their use cases, features and attributes, and potential customisation.
| G1 Standard |
G1 EDU |
G1-D Standard |
G1-D Flagship |
H1 Standard |
H1 EDU (H1-2) |
H2 Standard |
H2 EDU |
R1 AIR |
R1 Standard |
R1 EDU |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Images |

|

|

|

|

|
||||||
| Use Case | Consumer & Demonstration | Research & AI development | Industrial | Industrial & AI development | Consumer & Demonstration | Research & AI development | Consumer & Demonstration | Research & AI development | Consumer & Demonstration | Consumer & Demonstration | Research & AI development |
| DOF | 23 | 43 | 17 | 19 | 19 | 27 | 31 | 31 | 20 | 26 | 40 |
| Battery | 9Ah (hot-swap) | 9Ah (hot-swap) | 9Ah (hot-swap) | 30Ah | 15Ah | 15Ah | 15Ah | 15Ah | 5Ah (hot-swap) | 5Ah (hot-swap) | 5Ah (hot-swap) |
| Battery Life | 2h | 2h | 2h | 6h | 3h | 3h | 3h | 3h | 1h | 1h | 1h |
| Arm Payload | 2kg | 3kg | 3kg | 3kg | TBC | 7-21kg | 7-15kg | 7-15kg | 2kg | 2kg | 2kg |
| Maximum Speed | 2m/s | 2m/s | TBC | 1.5m/s | 5m/s | 5m/s | 2m/s | 2m/s | 3m/s | 3m/s | 3m/s |
| Compute | 8-core CPU | 8-core CPU / NVIDIA Jetson Orin NX GPU | 8-core CPU / NVIDIA Jetson Orin NX GPU | 8-core CPU / NVIDIA Jetson Orin NX GPU | 8-core CPU | 8-core CPU / NVIDIA Jetson Orin NX GPU | 8-core CPU | 8-core CPU / NVIDIA Jetson AGX Thor GPU | 8-core CPU | 8-core CPU | 8-core CPU / NVIDIA Jetson Orin NX GPU |
| AI | ✖ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✖ | ✔ | ✖ | ✔ | ✖ | ✖ | ✔ |
| Optional Hands | ✖ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✖ | ✔ | ✖ | ✖ | ✖ |
| Dimensions | 1320 x 450 x 200mm | 1320 x 450 x 200mm | 1260 x 500 x 500mm | 1260 x 525 x 570mm | (1520+2 8 5) 570 220mm | (1520+2 8 5) 570 220mm | 1820 x 456 x 218mm | 1820 x 456 x 218mm | 1230 x 357 x 190mm | 1230 x 357 x 190mm | 1230 x 357 x 190mm |
| Weight | 35kg | 35kg+ | 50kg | 80kg | 47kg | 70kg | 70kg | 70kg | 25kg | 29kg | 29kg |
| For specifications and additional information, please contact our sales team or visit the product pages. | |||||||||||
Physical AI
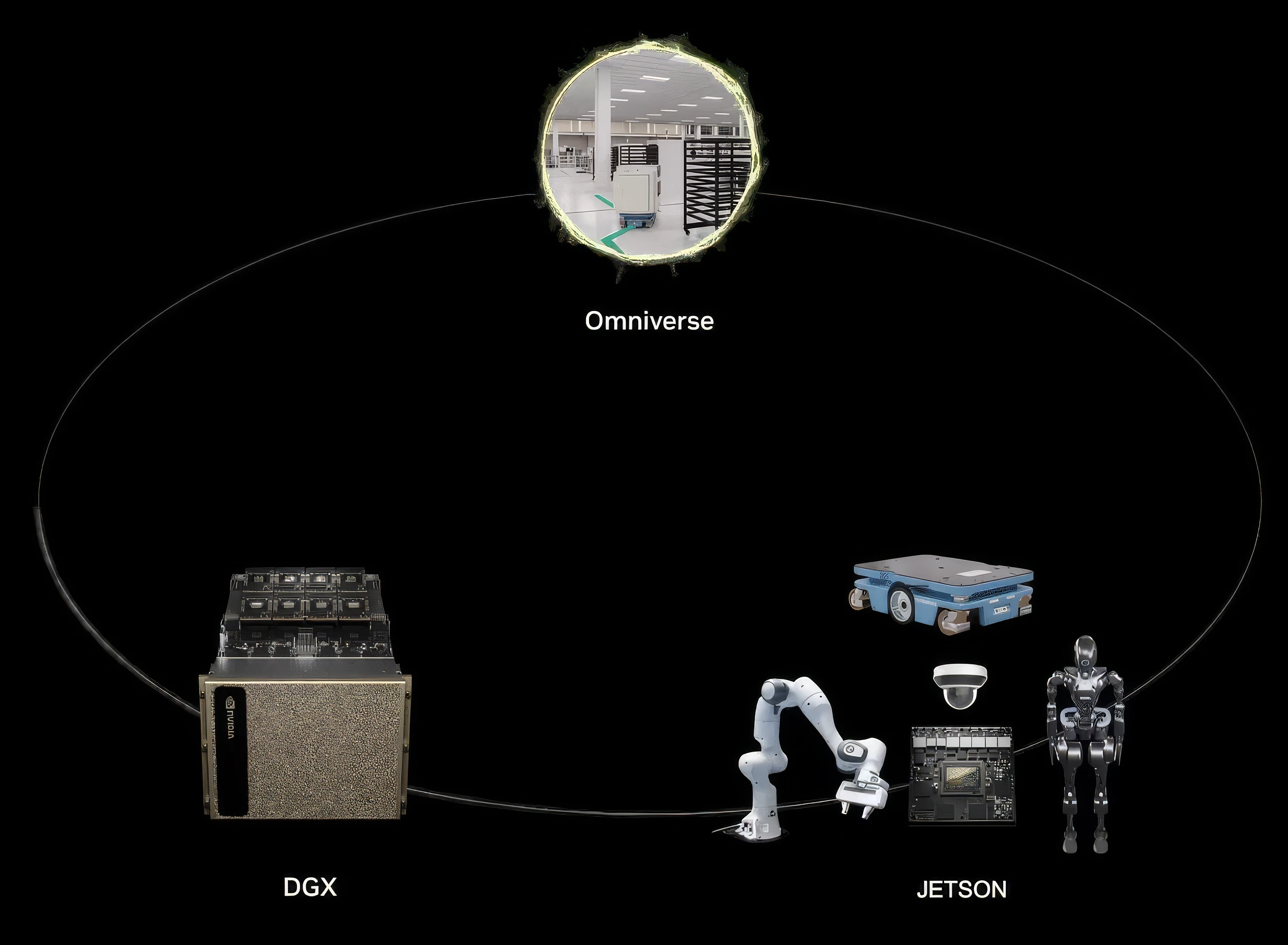
We mentioned physical AI at the start of this guide, but let’s recap. Physical systems (humanoid robots, quadruped robots or robotic arms) capture and process information from their sensors and actuators to perform their functions. However, if you want to introduce any degree of AI automation and learning, especially in complex environments then the data and processing demands demand a whole other level of performance. This is often referred to as the three-computer problem, or the three-computer solution, as three distinct levels of compute are required to achieve this - NVIDIA DGX, NVIDIA Omniverse and NVIDIA Jetson.
To explain why AI robotic systems are much more complicated than other types of AI model, imagine an algorithm designed to recognise five types of cooking utensil. This requires training a model to recognise cooking utensils and a camera sensor to see the various types. Now add in the ability to pick up these utensils and use them - the camera element now needs the addition of robotic arms and further training of how each utensil is used. Now add mobility so the robot can recognise, pick up and use the utensil, but only in the correct kitchen location - this adds more training on processes plus a spatial understanding of its environment. Finally, make the robot work in a crowded kitchen where it may be obstructed or knocked off balance mid-task - the training now needs to include how to negotiate obstacles and how to recover an interrupted task, without causing injury as some collisions may be with softer humans rather than harder surfaces.
You can see how the additional layers of complexity at each stage require a whole new level of training data and parameters to give the robot any chance of success. This is where the three computers come in - firstly, powerful multi-GPU DGX SYSTEMS are required to train datasets so large to scale and then fine-tune the model. Next, RTX PRO SERVERS - designed for advanced visualisation tasks - support the OMNIVERSE real-time collaboration cloud platform. This enables simulation of the environments and human-robot interactions, so all scenarios can be tried and tested. Most importantly, mistakes and errors can be ironed out in the Omniverse digital twin so costly real-world mishaps can be avoided. Finally, and as mentioned above in the humanoid and quadruped robot tabs, onboard JETSON modules allow the finalised model to be deployed directly on the robot so it can perform as intended.
Ready to Buy?
Scan, as a leading Unitree, DOBOT and NVIDIA Elite Partner, and the UK’s only NVIDIA DGX-certified Managed Services Partner, is ideally placed to be your trusted advisor on all your robotics and AI needs. Our expertise spans edge AI, sensor integration, autonomous navigation, and real-time inference — backed by a full ecosystem of hardware, software, simulation tools, and consultancy. We work closely with engineers, researchers, and innovators to deliver robotics solutions that are technically robust, commercially viable, and ready for the environments they’ll operate in.
Let’s Chat
Contact our expert teams on 01204 474210 or at [email protected], or visit our ROBOTICS WEBSITE. Alternatively browse our categories below.