Models, textures and applications are taking up more storage space every year, so it's important to select the optimum storage configuration for your workstation. This guide walks you through the pros and cons of the most common type of storage device. This guide will walk you through the pros and cons of the most common type of storage device. Choosing a faster storage device will not only make Windows boot faster, but will makes applications and models load quicker. Choosing an SSD is the ultimate upgrade, as it also makes your workstation more responsive in everything it does, not just loading new data.
| Storage Type | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solid State Drives | Hard Disk Drive | |||
| Pros | Fastest Storage Available, Silent | Big Capacity, Low Cost per GB | ||
| Cons | Highest Cost per GB | Slow, Audible | ||
| Recommended For | Boot drive and Performance Sensitive Data | Bulk Storage | ||

Solid State Drives (SSD)
Solid State Drives (SSDs) are the newest and fatest type of storage device, recording your data on memory chips rather than the spinning disks used in hard drives. This gives SSDs a huge edge when it comes to performance, although you do pay a higher cost per GB. Being solid state devices, SSDs barely consume any power and are silent, making them ideal for anybody wanting a quiet workstation. With no moving parts they're also a great choice for a laptop as are much tougher and lighter than HDDs. Early SSDs had a limited number of times they could be written to, but with current generation SSDs this is no longer a concern and you can expect to write data to an SSD for years.
SSDs are available in three main types as shown in the table below. Most SSDs are built using NAND memory chips and are available in two types, SATA or PCIe. The former are 2.5in drives that provide good performance and are ideal for bulk storage. The latter are M.2 drives and directly slot into the motherboard for much higher performance. As PCIe SSDs are more expensive than SATA SSDs we recommend prioritising them for performance senstive data such as the Operating System and caching. The third and final type of SSDs also use the PCIe bus, but are made from Optane memory chips. PCIe Optane SSDs read and write data a little slower than a PCIe NAND SSD, but have much lower latency so, if your application has lots of random rather than sequential data, a PCIe Optane SSD may actually be faster overall. However, PCIe Optane SSDs are more costly and not available in as large capacities as PCIe NAND SSDs.
 |
 |
 |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Memory Type | NAND | NAND | Optane | |||
| Bus | SATA | PCIe | PCIe | |||
| Form Factor | 2.5in | M.2 | 4x PCIe Card or U.2 | |||
| Read Speed | GOOD | BEST | BETTER | |||
| Write Speed | GOOD | BEST | BETTER | |||
| Latency | GOOD | BETTER | BEST |

Hard Disk Drives (HDD)
Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) have been around since the 1950s although back then they could only store a few MB, and now can store up to multiple TB. Hard drives have got a lot faster too, transferring data at around 150MB/sec, although this is till a fraction of the speed of an SSD. This makes HDDs the best type of bulk storage device for data such as documents and old projects. As mechanical devices, hard drives make some noise, so are best avoided if you want a really quiet system. If you need lots of storage, why not consider a NAS box, you can locate this small external device in another room, so you don't have to listen to the hard drives clattering away.
3XS Systems recommends Seagate HDDs in our workstations. Barracuda drives for standard use and the more expensive Barracuda Pro drives for mission critical data as these drives have higher endurance and a longer warranty.
 |
 |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Endurance | GOOD | BEST | ||
| Warranty | 2 Years | 5 Years |
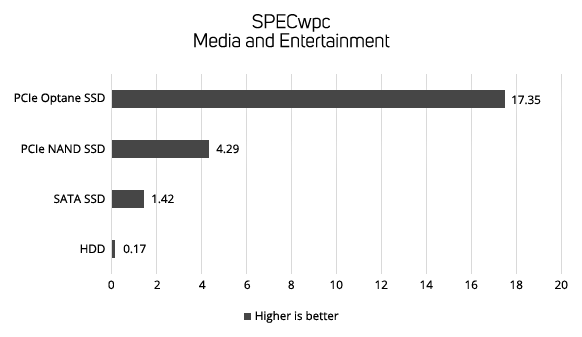
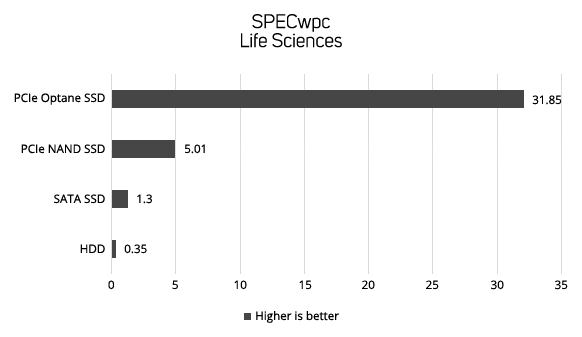
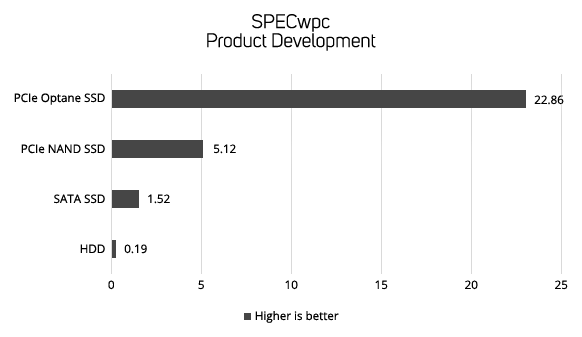
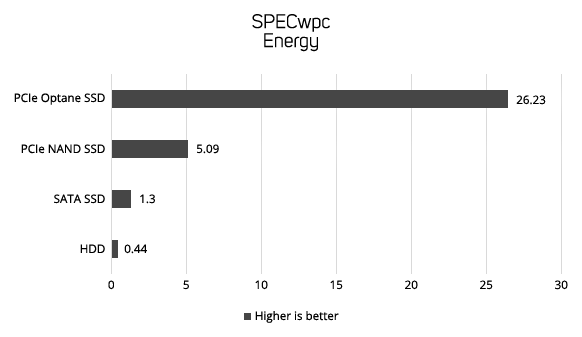
Drive Performance in Workstations
The following four graphs show the data transfer rate in MB/sec of the diferrent types of storage device in the industry standard SPECwpc benchmark. SPECwpc models the behaviour of different workstation applications, enabling you to see the relative performance difference between the different types of storage device.